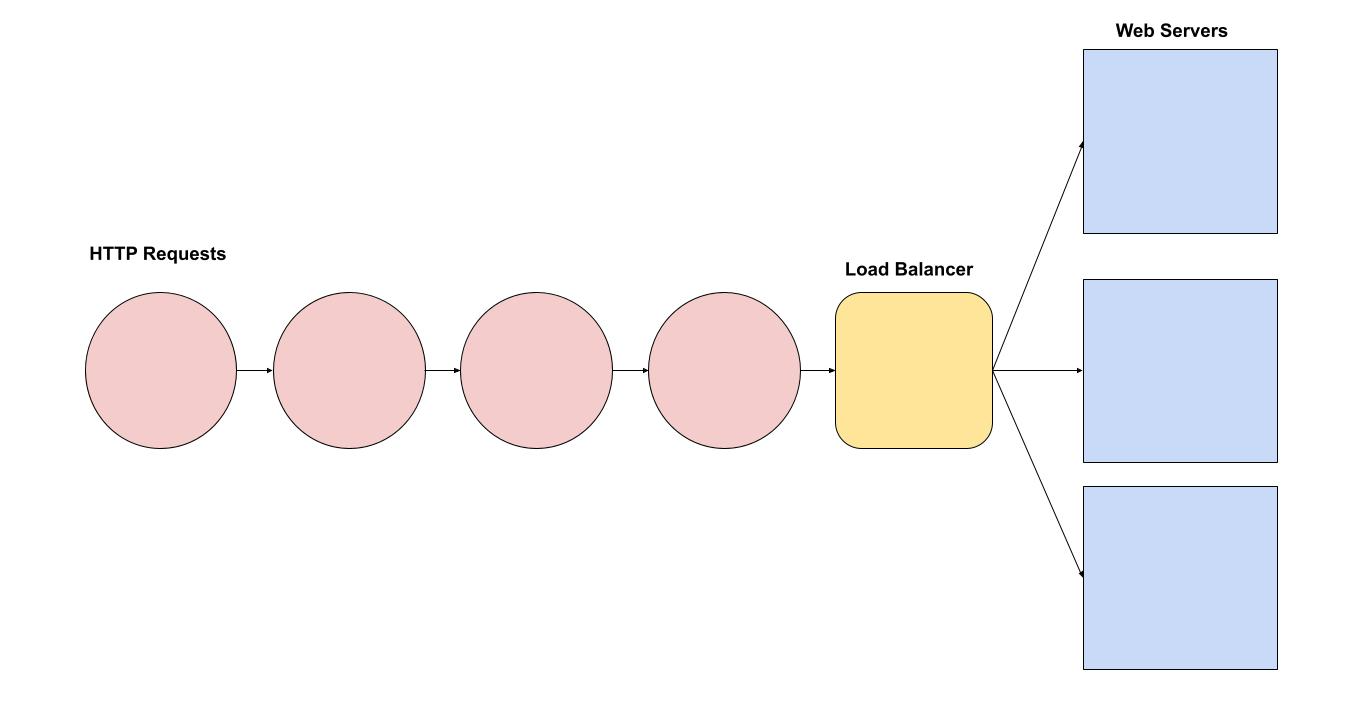
Imagine a busy store where many customers arrive at the same time to get help. To manage the crowd efficiently, the store uses a system to distribute customers to different available clerks. This system is like a load balancer for a web application.
Load Balancer Analogy
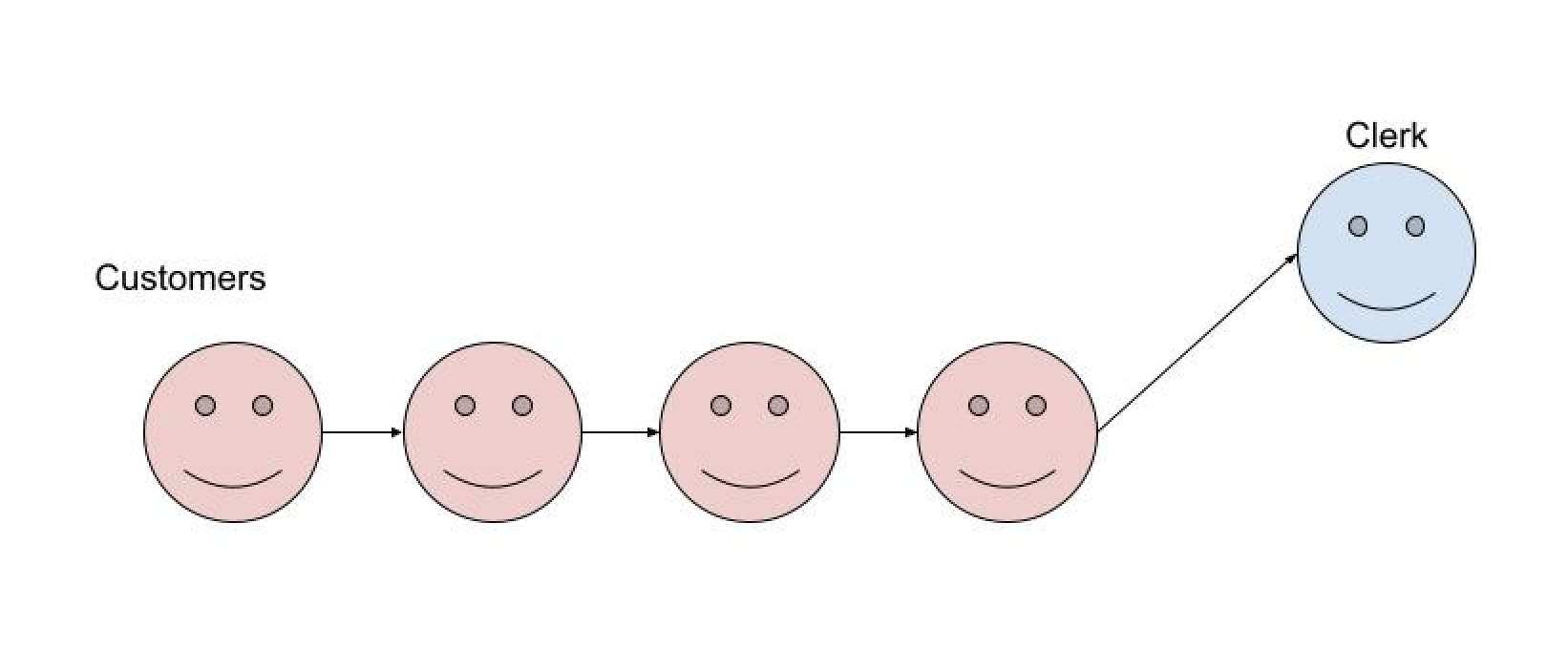
- Without a Load Balancer (Single Queue):
- All customers stand in a single line.
- One clerk at a time helps the next customer in line.
- If a clerk is busy, customers have to wait longer, even if other clerks are available.
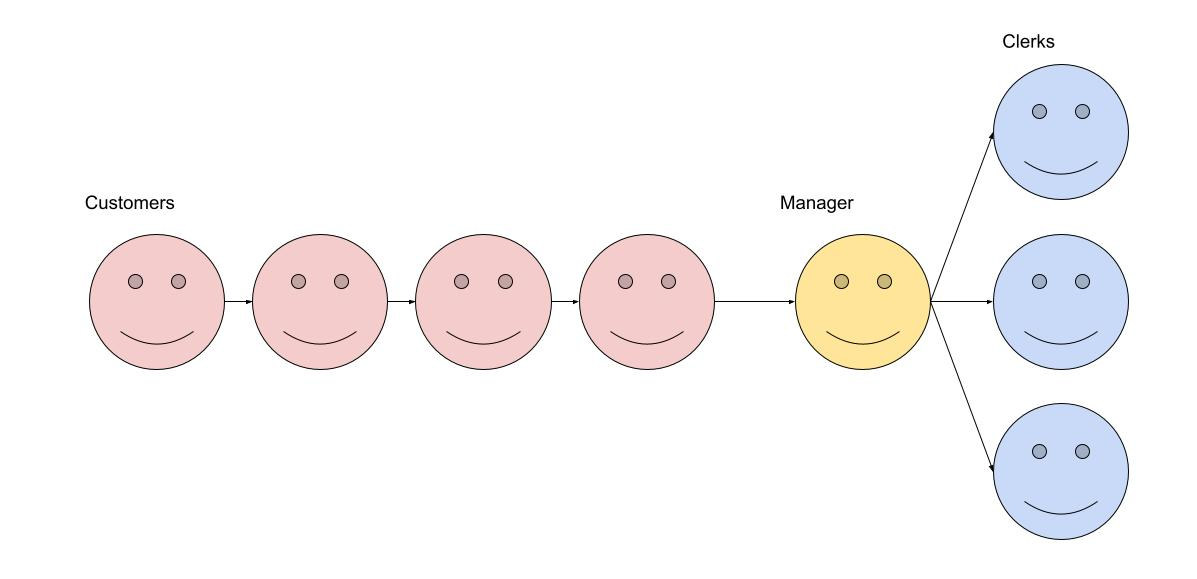
- With a Load Balancer (Multiple Queues):
- Customers arrive at the store.
- Instead of standing in one long line, there is a manager (the load balancer) at the entrance.
- The manager directs each customer to the next available clerk.
- This ensures that all clerks are working efficiently and customers are served as quickly as possible.
Key Points
- Efficiency: The load balancer (manager) makes sure no single clerk (server) gets overwhelmed while others are idle.
- Speed: Customers (requests) get served faster because they’re immediately directed to an open clerk (server).
- Balance: Work is evenly distributed among all clerks (servers), ensuring smooth operation.
Real-World Application
In a web application, a load balancer works similarly by distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers. This prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck, improves application availability, and ensures users get a smooth and fast experience.