Imagine a busy store where many customers arrive at the same time to get help. To manage the crowd efficiently, the store uses a system to distribute customers to different available clerks. This system is like a load balancer for a web application.
Load Balancer Analogy
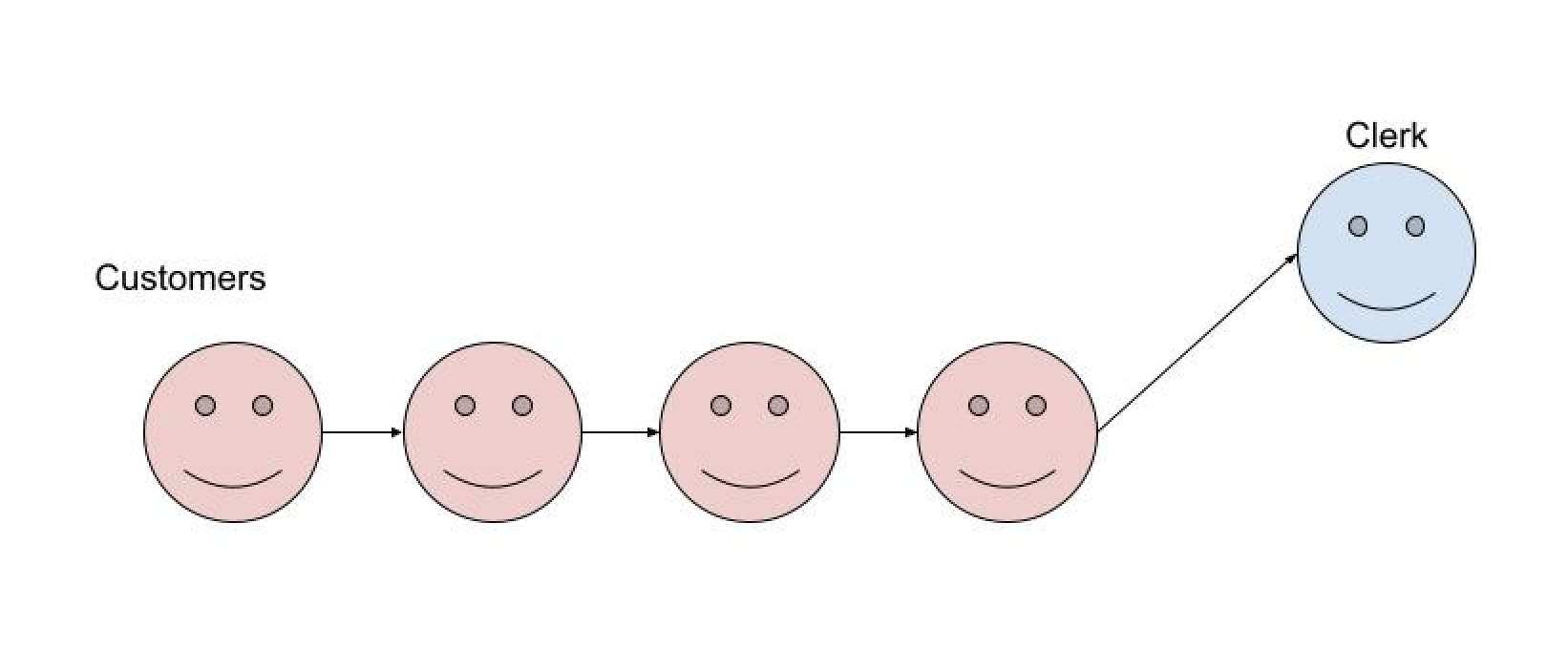
- Without a Load Balancer (Single Queue):
- All customers stand in a single line.
- One clerk at a time helps the next customer in line.
- If a clerk is busy, customers have to wait longer, even if other clerks are available.
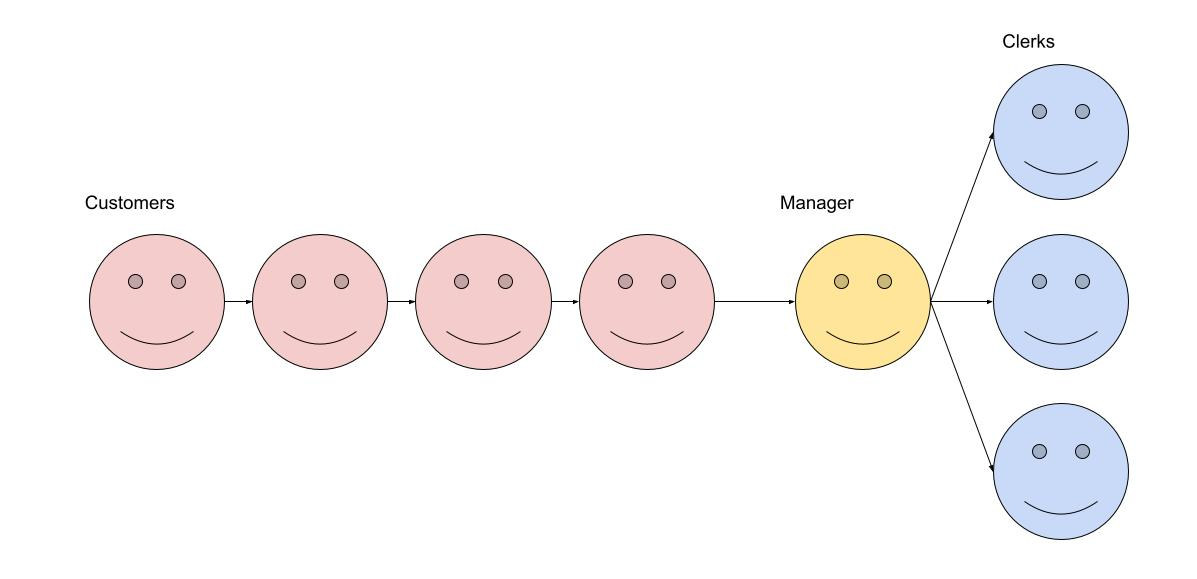
- With a Load Balancer (Multiple Queues):
- Customers arrive at the store.
- Instead of standing in one long line, there is a manager (the load balancer) at the entrance.
- The manager directs each customer to the next available clerk.
- This ensures that all clerks are working efficiently and customers are served as quickly as possible.
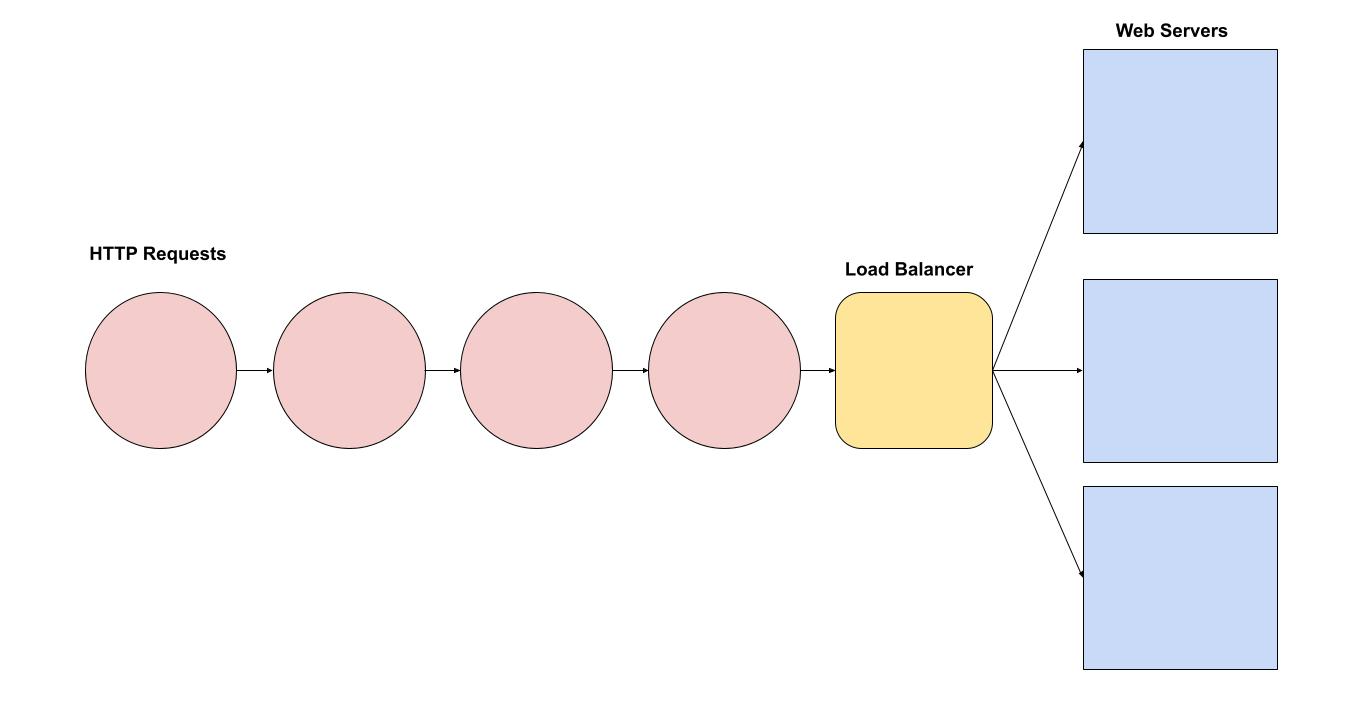
Key Points
- Efficiency: The load balancer (manager) makes sure no single clerk (server) gets overwhelmed while others are idle.
- Speed: Customers (requests) get served faster because they’re immediately directed to an open clerk (server).
- Balance: Work is evenly distributed among all clerks (servers), ensuring smooth operation.
Real-World Application
In a web application, a load balancer works similarly by distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers. This prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck, improves application availability, and ensures users get a smooth and fast experience.
Need Help Scaling Your Platform?
Whether you’re experiencing growing pains or planning for future traffic, we can help design and implement load balancing solutions that keep your application fast and reliable. Get in touch to discuss your infrastructure needs.
Learn more about our Infrastructure & Cloud Services.